Emotional variability is a natural part of being human. Our moods fluctuate in response to internal thoughts, external events, physical health, social interactions, and environmental stressors. While some degree of emotional change is healthy and adaptive, frequent or intense emotional swings can disrupt daily functioning, relationships, productivity, and overall mental well-being. One of the most effective and widely supported ways to stabilize emotional experiences is through the establishment of steady routines. Consistent daily patterns provide structure, predictability, and psychological safety, which play a crucial role in emotional regulation.
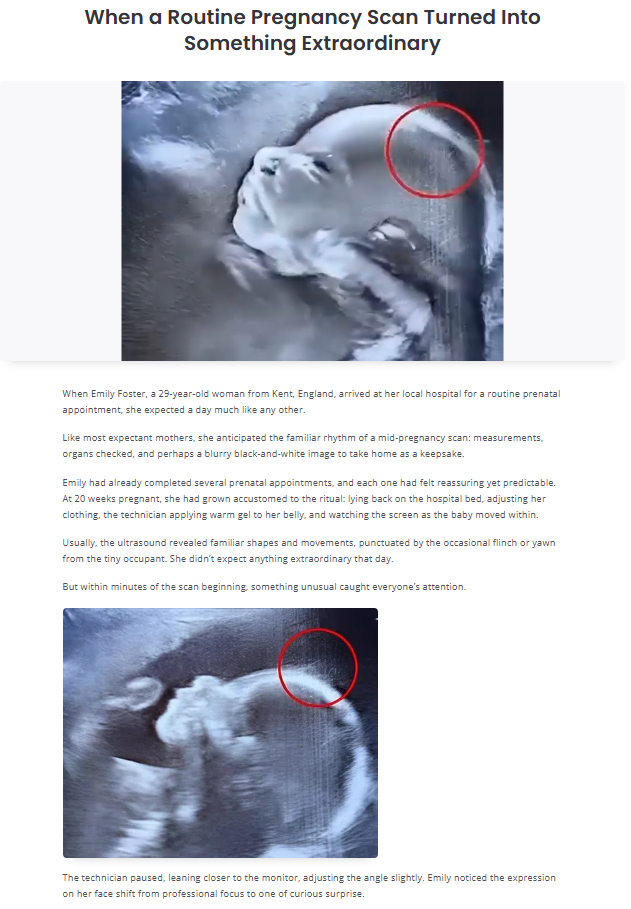
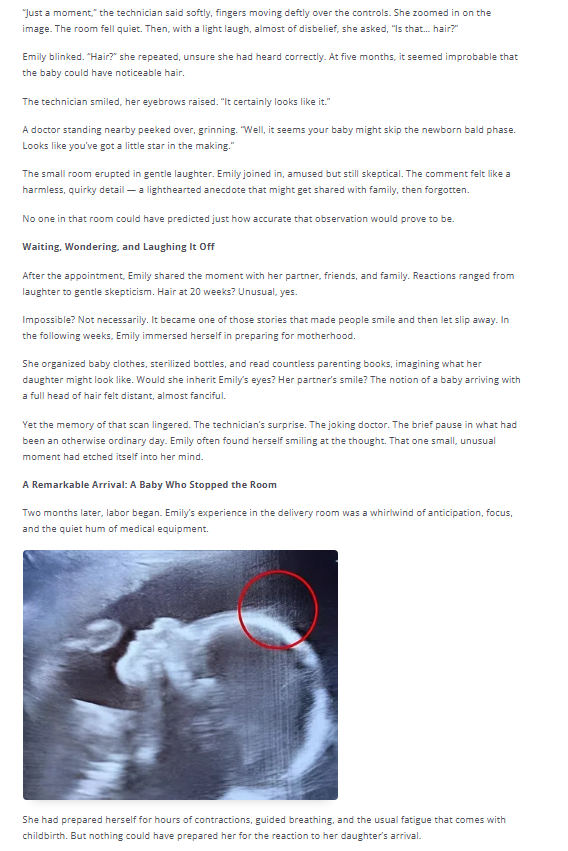
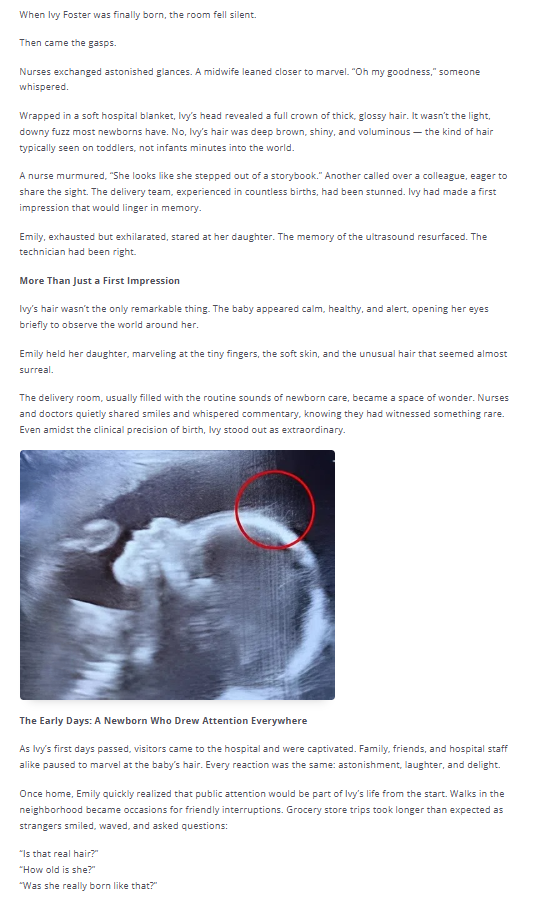
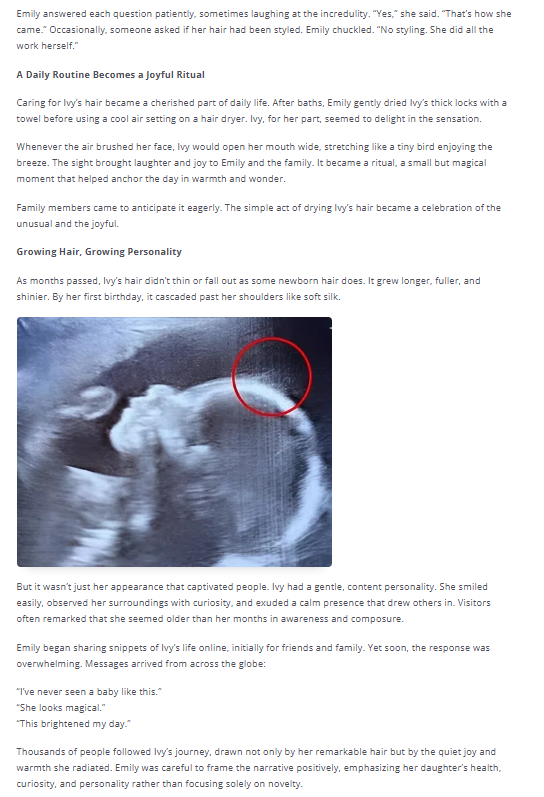
In modern life, where uncertainty, information overload, and constant demands are common, routines act as emotional anchors. They reduce the mental energy required to make decisions, create a sense of control, and help regulate the nervous system. Understanding why steady routines help manage emotional variability requires looking at how the brain processes predictability, how habits influence emotional responses, and how structured behaviors support mental resilience over time.
Understanding Emotional Variability
Emotional variability refers to the degree and frequency of changes in emotional states over time. While emotions naturally rise and fall, excessive variability may lead to feelings of instability, irritability, anxiety, or emotional exhaustion. People experiencing high emotional variability often feel reactive rather than responsive, meaning their emotions are easily triggered by minor stressors.
Several factors contribute to emotional variability, including stress, sleep disruption, irregular schedules, lack of self-care, and inconsistent daily habits. When life lacks structure, the brain remains in a constant state of alertness, scanning for what comes next. This heightened state can increase emotional reactivity and reduce the ability to self-regulate effectively.
Steady routines counteract these effects by offering consistency. They provide a framework that allows emotions to settle rather than fluctuate wildly in response to every change or challenge.
The Brain’s Need for Predictability
The human brain is wired to seek patterns and predict outcomes. Predictability helps the brain conserve energy and maintain emotional balance. When routines are consistent, the brain does not have to work as hard to anticipate what will happen next. This reduction in cognitive load directly impacts emotional regulation.
Unpredictable environments activate the brain’s stress response system, particularly the amygdala, which is responsible for detecting threats. Even minor unpredictability, such as irregular meal times or inconsistent sleep schedules, can subtly signal uncertainty to the brain. Over time, this can increase baseline stress levels and emotional volatility.
Steady routines send a different message. They communicate safety and reliability. When the brain knows what to expect, it shifts from a reactive mode to a more regulated state. This shift allows for better emotional control, improved focus, and a calmer baseline mood.
How Routines Regulate the Nervous System
Emotional variability is closely linked to the autonomic nervous system, which governs stress and relaxation responses. Irregular schedules can keep the nervous system stuck in a heightened state of arousal, making emotions more intense and harder to manage.
Consistent routines support nervous system regulation by reinforcing predictable cycles of activity and rest. Regular sleep and wake times, for example, help stabilize circadian rhythms, which influence mood-related neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. When these rhythms are disrupted, emotional balance often suffers.
Daily routines also encourage repeated exposure to calming behaviors, such as morning rituals, movement, meals, or wind-down practices. Over time, these repeated patterns condition the body to transition more smoothly between states of alertness and relaxation, reducing emotional spikes and crashes.
Decision Fatigue and Emotional Stability
One often-overlooked contributor to emotional variability is decision fatigue. Every decision, no matter how small, requires mental energy. When daily life is unstructured, individuals are forced to make constant choices about what to do next, when to eat, when to rest, and how to prioritize tasks.
This constant decision-making depletes cognitive resources and lowers emotional tolerance. As mental fatigue increases, people become more emotionally reactive, impatient, and overwhelmed. Minor frustrations feel larger, and coping capacity diminishes.
Steady routines reduce the number of decisions required throughout the day. When certain actions are habitual, they no longer require conscious effort. This conservation of mental energy allows individuals to respond to emotional challenges with greater clarity and calmness rather than impulsivity or distress.
Routines as Emotional Anchors
In times of emotional turbulence, routines serve as grounding mechanisms. They provide a sense of continuity when emotions feel chaotic. Even when internal states fluctuate, external consistency offers stability.
For individuals experiencing anxiety, depression, or high stress, routines can act as emotional anchors that prevent complete emotional derailment. Simple, predictable actions such as preparing breakfast, taking a daily walk, or following a consistent work schedule can create moments of normalcy and reassurance.
These anchors are especially important during periods of change or uncertainty. When external circumstances are unpredictable, maintaining even small routines can preserve emotional balance and prevent excessive variability.
Building Emotional Awareness Through Routine
Steady routines also enhance emotional awareness. When daily patterns are consistent, it becomes easier to notice emotional changes and identify their causes. In contrast, chaotic schedules can obscure emotional patterns, making it difficult to determine whether mood shifts are due to internal feelings or external disruptions.
Consistent routines create a stable baseline against which emotional changes can be measured. This clarity supports healthier emotional processing and allows individuals to address emotional needs more effectively. Over time, this awareness strengthens emotional intelligence and self-regulation skills.
The Role of Habits in Long-Term Emotional Regulation
Routines are closely tied to habits, and habits shape emotional responses over time. Repeated behaviors reinforce neural pathways in the brain, making certain emotional reactions more automatic. Positive routines gradually train the brain to associate stability with safety and calm.
For example, a consistent bedtime routine not only improves sleep but also signals to the brain that it is time to relax. Similarly, regular physical activity becomes associated with emotional release and mood improvement. These habitual associations reduce emotional variability by providing reliable methods for emotional regulation.
Importantly, routines do not eliminate emotions or suppress emotional expression. Instead, they create conditions in which emotions can be experienced without becoming overwhelming or destabilizing.
Flexibility Within Structure
While routines are powerful tools for emotional stability, they are most effective when balanced with flexibility. Rigid schedules that leave no room for adaptation can become sources of stress themselves. The goal is not perfection but consistency.
Healthy routines allow for variation without losing their core structure. This balance teaches emotional resilience by reinforcing stability while accommodating change. Over time, individuals learn that emotional steadiness does not require control over every detail but rather a reliable foundation that supports adaptation.
Long-Term Benefits of Steady Routines
The long-term impact of steady routines on emotional variability extends beyond daily mood regulation. Consistent routines improve sleep quality, enhance focus, strengthen self-discipline, and increase overall life satisfaction. These factors collectively contribute to greater emotional resilience and reduced vulnerability to mood disturbances.
Over time, individuals with steady routines often experience improved confidence in their ability to manage emotions. This sense of competence further reduces emotional volatility, creating a positive feedback loop of stability and well-being.
Conclusion
Steady routines play a vital role in managing emotional variability by providing structure, predictability, and psychological safety. They support brain function, regulate the nervous system, reduce decision fatigue, and create emotional anchors in an otherwise unpredictable world. Rather than restricting freedom, routines offer a stable framework that allows emotions to flow without overwhelming the individual.
In a fast-paced and uncertain environment, consistent daily patterns are not a sign of rigidity but a powerful form of self-care. By cultivating steady routines, individuals can experience greater emotional balance, improved resilience, and a more grounded connection to their daily lives. Over time, these benefits accumulate, transforming routines into essential tools for long-term emotional health and stability.



