In a world defined by constant change, emotional endurance has become an essential human capacity. Emotional endurance refers to the ability to sustain psychological stability, resilience, and inner balance during prolonged stress, uncertainty, or adversity. One of the most overlooked yet powerful contributors to emotional endurance is rhythm—specifically, steady rhythms that structure our bodies, minds, and environments. From biological processes to daily routines and cultural practices, steady rhythms play a vital role in helping individuals regulate emotions, maintain focus, and endure life’s challenges with greater resilience.

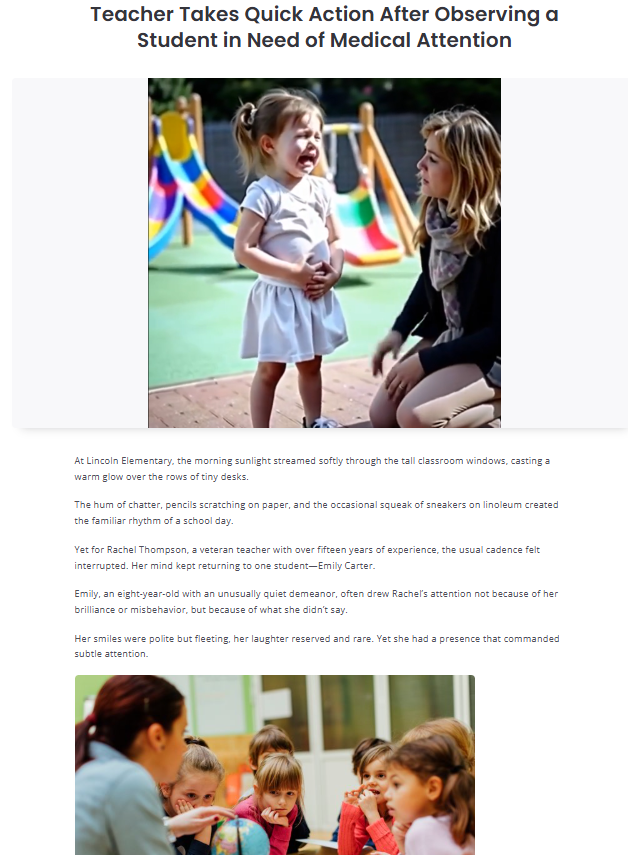


Steady rhythms are repeating, predictable patterns that occur over time. These patterns can be biological, such as breathing and heartbeats; behavioral, such as sleep cycles and daily routines; or external, such as music, movement, and environmental cues. When these rhythms are stable, they provide a sense of continuity and safety, allowing the nervous system to remain regulated. This regulation is foundational for emotional endurance, as emotional stability depends heavily on the body’s ability to manage stress responses effectively.
At the biological level, the human body is governed by rhythms. The circadian rhythm, which regulates sleep and wake cycles, is one of the most influential. When this rhythm is consistent, the body produces hormones like cortisol and melatonin in balanced ways, supporting mood regulation and mental clarity. Disruptions to circadian rhythms, such as irregular sleep patterns or prolonged exposure to artificial light, are strongly associated with emotional dysregulation, anxiety, and burnout. In contrast, maintaining a steady sleep-wake rhythm enhances emotional stamina by ensuring the brain has adequate time to recover and process emotional experiences.
Breathing rhythm is another critical yet often unconscious factor in emotional endurance. Slow, steady breathing sends signals to the brain that the body is safe, activating the parasympathetic nervous system. This physiological response reduces stress hormones and promotes calmness. Over time, individuals who naturally or intentionally adopt steady breathing patterns tend to experience greater emotional control, especially during high-pressure situations. This explains why rhythmic breathing techniques are widely used in stress management, meditation, and therapeutic practices.
Beyond biology, steady rhythms in daily life contribute significantly to emotional resilience. Consistent routines provide predictability, which reduces cognitive and emotional load. When individuals know what to expect from their day, they expend less mental energy on decision-making and uncertainty. This conservation of emotional resources allows them to cope more effectively with unexpected challenges. Even simple routines, such as eating meals at regular times or engaging in a consistent morning practice, can create a stabilizing effect that strengthens emotional endurance over time.
Work and productivity rhythms also influence emotional sustainability. Continuous overexertion without structured pauses often leads to emotional exhaustion. In contrast, steady cycles of focused work followed by rest allow the mind to recover and reset. This rhythm prevents emotional depletion and supports long-term engagement rather than short-lived bursts of effort. Emotional endurance is not built through constant intensity, but through balanced, repeatable patterns that respect human limits.
Music and movement provide another powerful example of how steady rhythms support emotional strength. Rhythmic music has been shown to synchronize brain activity and influence emotional states. Steady tempos can calm the nervous system, reduce anxiety, and foster emotional grounding. Similarly, rhythmic physical activities such as walking, swimming, or dancing create a flow state where emotions are processed naturally and without overwhelm. These activities offer a safe outlet for emotional expression while reinforcing internal stability.
Culturally, rhythm has always played a role in emotional endurance. Many traditional societies rely on rituals, ceremonies, and communal practices that follow steady rhythmic patterns. These shared rhythms foster a sense of belonging and continuity, which buffers individuals against emotional distress. When people participate in collective rhythms, they feel less isolated in their struggles, enhancing their capacity to endure hardship. Even in modern contexts, group activities with rhythmic elements can restore emotional balance and reinforce social support.
Psychologically, steady rhythms help the brain make sense of time and experience. Emotional distress often intensifies when time feels chaotic or overwhelming. Rhythms segment time into manageable units, allowing the mind to process experiences incrementally. This structured perception of time reduces emotional overload and supports endurance by making challenges feel more navigable. Over time, the brain learns to associate steady rhythms with safety, reinforcing emotional stability during future stressors.
Another important aspect of rhythm is its role in emotional regulation through repetition. Repeated rhythmic experiences create neural pathways that promote calm and focus. When an individual repeatedly engages in steady patterns, such as consistent exercise or regular mindfulness practices, the brain adapts by strengthening emotional control mechanisms. This neurological reinforcement means that emotional endurance becomes less effortful and more automatic over time.
Modern life, however, often disrupts natural rhythms. Irregular schedules, constant digital stimulation, and social pressures can fragment attention and destabilize emotional patterns. This disruption makes emotional endurance harder to sustain. Reintroducing steady rhythms into daily life acts as a counterbalance, restoring a sense of order and predictability. Even small changes, such as limiting screen use at night or establishing consistent meal times, can have a profound impact on emotional resilience.
It is important to note that steady rhythms do not imply rigidity. Emotional endurance thrives on rhythms that are flexible yet consistent. Healthy rhythms allow for adaptation without collapsing into chaos. This balance enables individuals to remain emotionally grounded while responding effectively to change. Emotional endurance, therefore, is not about resisting emotions but about having a stable internal framework that can hold them.
Over time, the cumulative effect of steady rhythms becomes deeply transformative. Individuals who live in alignment with consistent patterns often report greater emotional clarity, reduced anxiety, and improved stress tolerance. These benefits compound, creating a feedback loop where emotional endurance further reinforces healthy rhythms. This cycle supports not only mental well-being but also physical health, relationships, and overall life satisfaction.
In conclusion, steady rhythms are foundational to emotional endurance. They regulate biological processes, stabilize daily life, support psychological resilience, and foster emotional balance. In a fast-paced and unpredictable world, cultivating steady rhythms offers a practical and sustainable way to strengthen emotional stamina. By aligning with predictable patterns in sleep, breathing, movement, and routine, individuals can build the emotional endurance necessary to navigate life’s challenges with greater calm, clarity, and resilience.



